Scars of tectonic extension promote ice-sheet nucleation from Hercules Dome, West Antarctica
Abstract
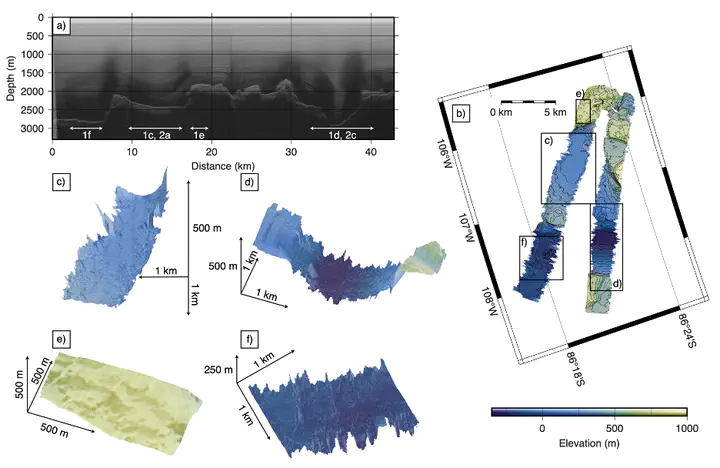
Geology and bed topography influence how ice sheets respond to climate change. Despite the West Antarctic Ice Sheet’s capacity to retreat and advance quickly over its over-deepened interior, little is known about the subglacial landscape of the East Antarctic elevated interior that probably seeded West Antarctic ice streams and glaciers. At Hercules Dome, we use three-dimensional swath radar technology to image the upstream origin of large subglacial basins that drain ice from the Antarctic interior into West Antarctic ice streams. Radar imaging reveals an ancient, alpine landscape with hanging tributary valleys and large U-shaped valleys. On the valley floors, we image subglacial landforms that are typically associated with temperate basal conditions and fast ice flow. Formation mechanisms for these subglacial landforms are fundamentally inconsistent with the currently slowly flowing ice. Regional aerogravity shows that these valleys feed into larger subglacial basins that host thick sediment columns. Past tectonism probably created these basins and promoted ice flow from Hercules Dome into the Ross and Filchner–Ronne sectors. This suggests that the landscape at Hercules Dome was shaped by fast-flowing ice in the past when the area may have served as or been proximal to a nucleation centre for the West Antarctic Ice Sheet.