Subglacial Hydrology
Subglacial Hydrology Observation
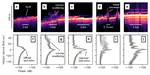
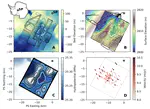
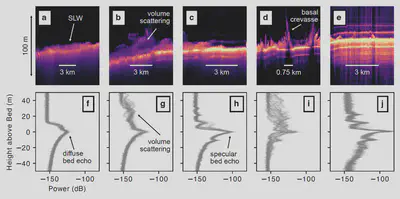
Radar sounding is one of the predominant geophysical tools used for investigating subglacial lakes. However, lake locations identified with radar have not coincided with lakes identified at the surface with spaceborne lidar methods. We found that volume scattering on small water inclusions in temperate ice directly above the lake lid are suppressing the radar echo from the lake and therefore obscuring the lake from the radar image.
Subglacial Hydrology Modeling
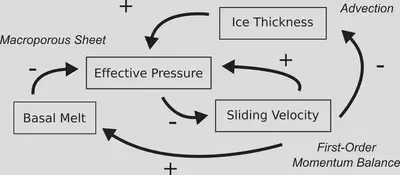
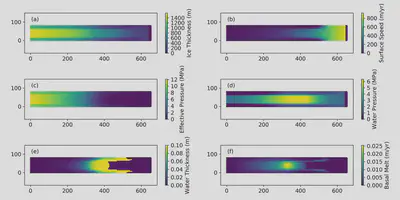
Numerical models of subglacial hydrologic systems typically distinguish between two end-member drainage systems. Distributed systems include slow drainage through thin water films at the ice-bed interface, flow through porous sediment layers, or linked cavity networks where water occupies cavities on the lee side of bedrock bumps. Channelized systems consist of efficient conduits, often modeled as Röthlisberger channels (R-channels) carved into basal ice or Nye channels incised into bedrock. Real subglacial systems often contain elements of both, and capturing the transition between these states is a key modeling challenge.